-
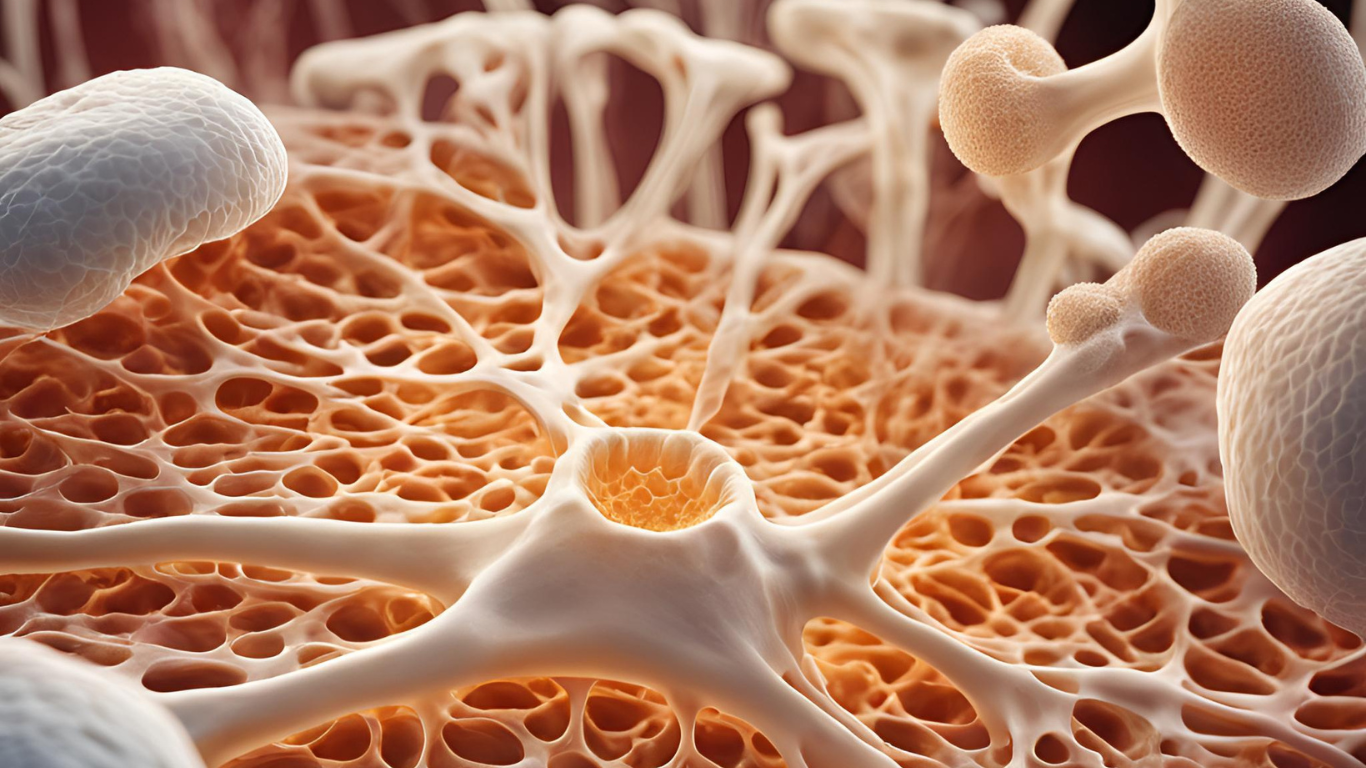
Ossification
Ever wondered how bones actually form? Let’s explore the journey of bone formation, focusing on intramembranous and endochondral ossification. From early development in fetal life to the continuous process in adulthood, bone formation is a detailed and impressive process. Ossification, or bone formation, starts in fetal life when existing connective tissue is replaced. Intramembranous ossification Continue reading
-
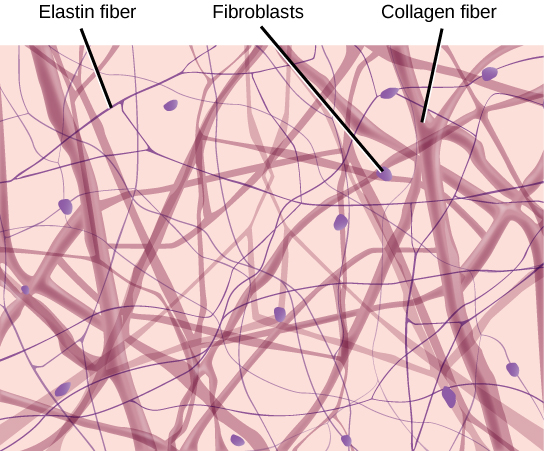

Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is the unsung hero of our body, holding everything together and ensuring smooth operation. It binds tissues and supports metabolic exchanges, thanks to its rich mix of collagen and glycosaminoglycans. This dynamic matrix not only maintains tissue strength but also defends against threats. Thus, by exploring its crucial role, we uncover its significance Continue reading
Category: Connective tissue
Connective tissue – The biological glue: Exploring the most diverse and abundant tissue type responsible for support, protection, and integration.
Connective tissue (CT) is the framework of the body. Unlike epithelial tissue, which is characterized by closely packed cells, CT consists of cells scattered throughout an extensive Extracellular Matrix (ECM). This matrix determines the tissue’s physical properties, ranging from the fluid nature of blood to the rigidity of bone.
The Three Structural Elements
All CT (except blood and lymph) are composed of three primary components:
- Cells: Such as fibroblasts, adipocytes, and immune cells.
- Protein Fibers: Collagen (strength), Elastic (flexibility), and Reticular (support).
- Ground Substance: The clear, viscous fluid that fills the space between cells and fibers.
Classification of Connective Tissue
- •
Connective Tissue Proper: Includes Loose (Areolar, Adipose, Reticular) and Dense (Regular, Irregular, Elastic) tissues. - •
Supporting CT: Provides structure via Cartilage (Hyaline, Fibrocartilage, Elastic) and Bone (Osseous tissue). - •
Fluid CT: Blood and Lymph, specialized for the transport of nutrients, gases, and wastes.
Clinical Focus
CT is often the site of inflammatory and immune responses. Understanding its composition is critical for diagnosing Connective Tissue Diseases (CTDs) like Lupus, Rheumatoid Arthritis, and Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome.