-
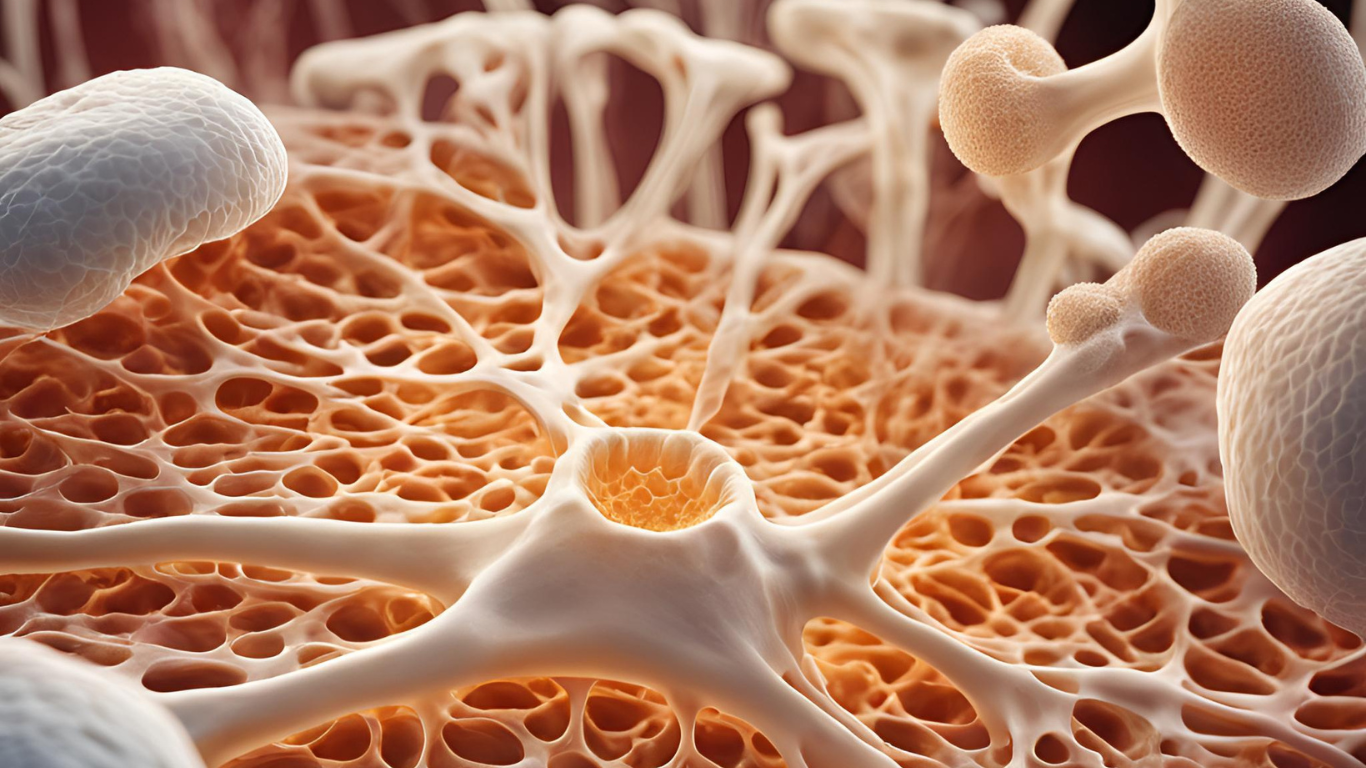
Ossification
Ever wondered how bones actually form? Let’s explore the journey of bone formation, focusing on intramembranous and endochondral ossification. From early development in fetal life to the continuous process in adulthood, bone formation is a detailed and impressive process. Ossification, or bone formation, starts in fetal life when existing connective tissue is replaced. Intramembranous ossification Continue reading
-
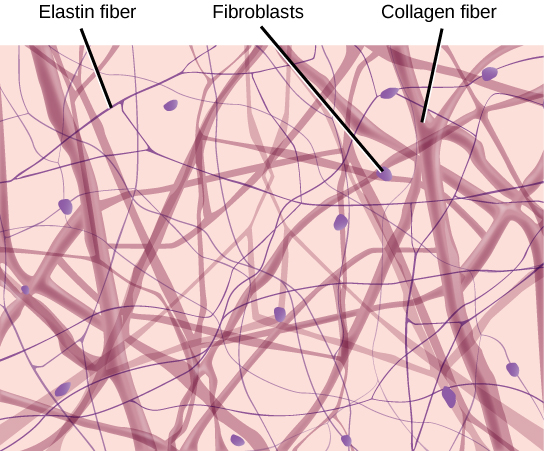

Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is the unsung hero of our body, holding everything together and ensuring smooth operation. It binds tissues and supports metabolic exchanges, thanks to its rich mix of collagen and glycosaminoglycans. This dynamic matrix not only maintains tissue strength but also defends against threats. Thus, by exploring its crucial role, we uncover its significance Continue reading
-
Types of Glands
Glands are fascinating and essential parts of our bodies, each with unique roles and features. They can be classified based on their structure, similar to the epithelia, but also the type of secretion they produce, and how they release it. Understanding these differences helps us appreciate how our bodies function and stay healthy. Let’s dive Continue reading
-
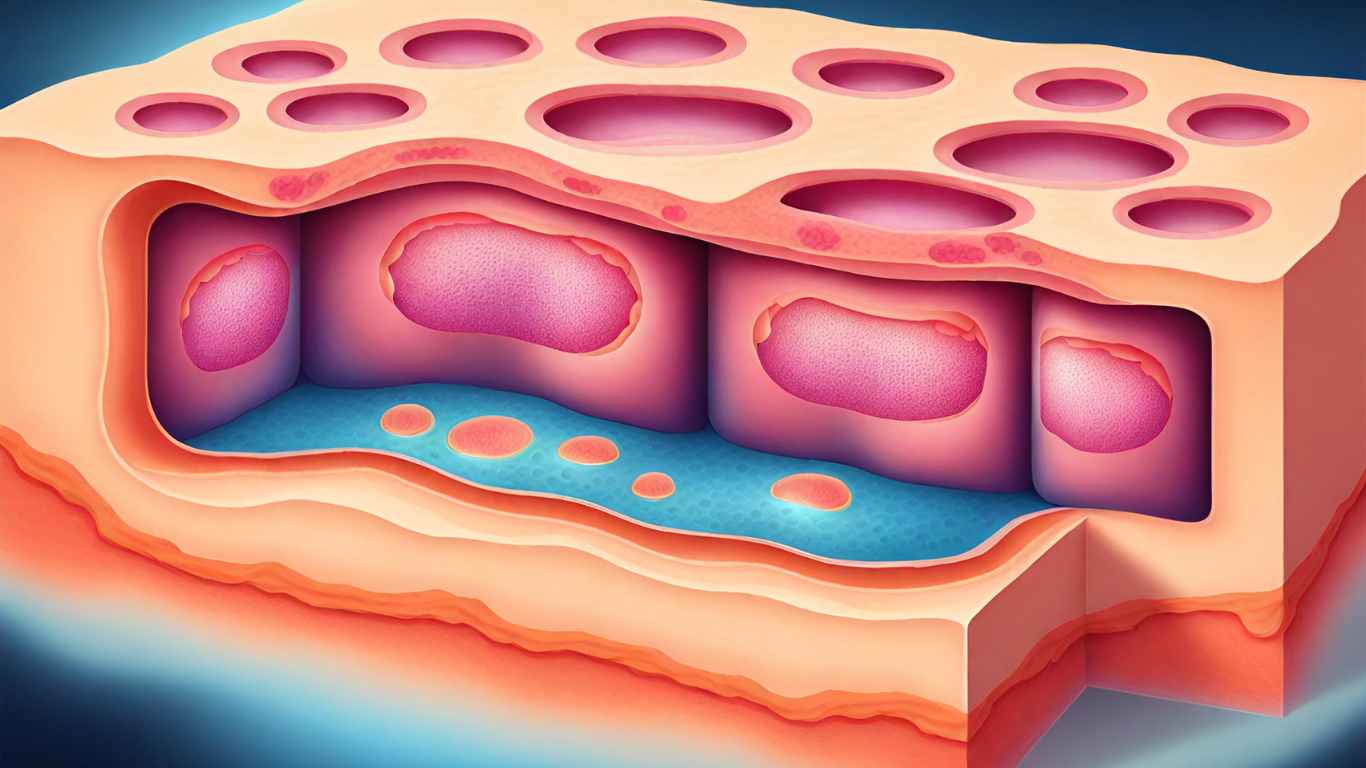
Types of Epithelium
Epithelium is what covers all the internal and external surfaces of our bodies. This article dives into the diverse types of epithelium, from simple squamous to transitional, understanding their structures and functions. Learn about their locations and roles in various bodily systems. To learn how to correctly identify and name epithelia, see the article on Continue reading
Category: Tissues of the body
From proliferation to specialization: Understanding how differentiated cell groups form the functional building blocks of the human body.
Cells divide and proliferate, giving rise to specialized groups that carry out distinct biological roles. These organized collectives are known as tissues, representing the vital bridge between individual cells and complex organs.
Definition
A tissue is a group of cells with similar structure and function, working in synergy to perform specific tasks. These tissues are further organized into organs, essential for maintaining physiological homeostasis.
Primary Tissue Classification
In the human body, tissues are categorized into four primary types, each possessing distinct characteristics:
- •
Epithelial Tissue: Covers body surfaces and lines hollow organs and cavities. - •
Connective Tissue: Protects, supports, and binds structures together. - •
Muscle Tissue: Specialized for contraction and the generation of force. - •
Nervous Tissue: Detects changes in conditions and transmits electrical signals.
Each tissue type contributes uniquely to the overall health and function of the organism. Understanding these cellular foundations is the first step toward mastering histopathology and clinical diagnostics.